python_note
global(全局) nonlocal(嵌套函数)
IO
1 | |
自定义排序
1 | |
对于cmp(this,other), 如果返回为负值,则将this元素排列到输出列表前面
1 | |
enumerate
1 | |
排列组合
全组合
1 | |
output:ab ac bc
全排列
1 | |
解包
*list 去除括号
1 | |
String
format
{a:.2f}保留a小数点后两位1
2>>> f"{a:8.1f}"
' 123.5'{a:<10d}左对齐 (宽度为10){a:0>2d}数字右对齐,并补零 (宽度为2) e.g. 5 -> 05
进制
b:二进制;o:八进制;d:十进制;x:十六进制
其他进制转十进制
1 | |
十进制转其他进制
1 | |
双向队列
collections.deque([iterable[,maxlen]])
1 | |
但deque不支持切片slice操作
计数器
collections.counter
1 | |
最大公约数
math.gcd(*integers)
最小公倍数
math.lcm(*integers)
n!
math.factorial(n)
二分 bisect
前提:列表有序
使用 bisect 模块的方法之前,须确保待操作对象是 有序序列
bisect.bisect_left(array, x, [lo=0, hi=len(a)])
- 找出插在最靠近x之前的位置,lo/hi上下限
heapq最小堆
import heapq
创建堆
- a=[]
- a=heapify(x) :一个列表转化为小根堆
1
2heapq.heappush(a,18)
heappop(a)nlargest(n , iterbale, key=None) / nsmallest(n , iterbale, key=None)
获取列表中最大、最小的几个值
1
2
3a = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 7, 8, 10, 15, 20, 25]
heapq.nlargest(5,a)
# [25, 20, 15, 10, 8]
数论
质数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7n = eval(input())
primes = [1]*n
primes[0]=primes[1]=0
for i in range(2,int(n**0.5)+1):
if primes[i]:
primes[i*i:n:i]=[0]*((n-i*i-1)//i+1)
print(sum(primes))扩展欧几里得
- ax+by=gcd(a,b)
1
2
3
4
5
6def exgcd(a, b):
if b == 0:
return 1, 0, a
x, y, g = exgcd(b, a % b)
x, y = y, x - a // b * y
return x, y, g
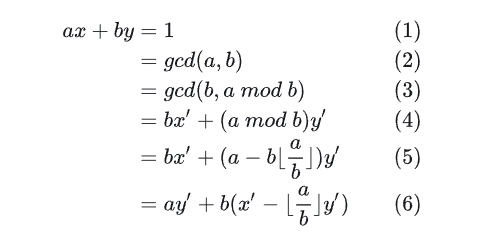
快速幂
pow(a,b,z)= a^b%z
IDLE settings
*Python
打开目录下的config-extensions.def文件
[AutoComplete] enable=1 popupwait=0
找到
AutoComplete.py"""Complete either attribute names or file names. Either on demand or after a user-selected delay after a key character, pop up a list of candidates. """ import os import string import sys
python_note
http://example.com/2024/06/30/python-note/